Municipal Debt Characteristics – Series 7 Exam
- April 1, 2025
- Posted by: 'FINRA Exam Mastery'
- Category: Finance
No Comments
🧾 Municipal Debt Characteristics – Series 7 Exam
📘 Key Features of Municipal Bonds You Must Know for the Series 7
Municipal debt securities (often called “munis”) are an important topic on the Series 7 exam. Understanding how they work, their tax benefits, risks, and types will help you answer several questions confidently. Here’s a clean, focused summary of the municipal debt characteristics you need to know.
🎯 1. What Are Municipal Bonds?
- Issued by state and local governments, and their agencies.
- Used to finance public projects like schools, highways, hospitals, and water systems.
- Interest income is generally exempt from federal income tax, and may also be exempt from state and local taxes if the investor lives in the issuing state.
🎯 2. Types of Municipal Bonds
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| General Obligation Bonds (GOs) | Backed by the full taxing power of the issuer (income, property, sales taxes). |
| Revenue Bonds | Supported by revenues from specific projects (e.g., toll roads, airports). |
| Special Tax Bonds | Secured by taxes other than ad valorem (like gas or tobacco taxes). |
| Special Assessment Bonds | Paid from charges on the benefitting property owners (like sewer projects). |
| Moral Obligation Bonds | State has a moral, but not legal, obligation to pay debt if the issuer cannot. |
| Private Activity Bonds | Used for private projects (like stadiums), may be subject to AMT (Alternative Minimum Tax). |
🎯 3. Key Characteristics of Municipal Bonds
- Interest Income:
Generally federally tax-exempt; might also be state- and local tax-exempt if purchased in the investor’s state of residence. - Credit Risk:
Revenue bonds carry more risk than GOs because they depend on project success. - Marketability:
Some municipal bonds are less liquid than Treasury or corporate bonds, especially smaller or locally issued bonds. - Pricing and Quoting:
Quoted as a percentage of par (e.g., 98 = $980). - Taxable Municipal Bonds:
In some cases, if a municipal bond is not qualified for federal tax exemption, it may be issued as taxable.
🎯 4. Tax Considerations
- Triple Tax-Free:
A municipal bond may be free from federal, state, and local taxes if purchased by a resident in the issuing locality. - Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT):
Interest from private activity bonds may be taxable under the AMT calculation. - Tax Equivalent Yield:
Investors often compare the yield on a muni bond to a taxable bond to determine value. Formula:
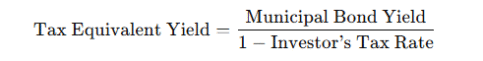
Example:
- 4% muni bond yield
- 30% tax bracket
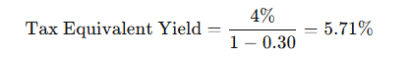
🎯 5. Risk Factors in Municipal Bonds
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Credit Risk | Risk that issuer cannot pay principal/interest. |
| Market Risk | Prices fluctuate based on interest rate movements. |
| Liquidity Risk | Difficulty selling bonds quickly without price discount. |
| Call Risk | Bonds may be called early if interest rates decline. |
🎯 6. Special Structures
- Variable Rate Demand Obligations (VRDOs):
Long-term municipal bonds with adjustable interest rates reset periodically. - Auction Rate Securities (ARS):
Interest rates reset through a Dutch auction; have liquidity risk if auctions fail.
🚀 Conclusion: What to Focus on for Series 7
- Understand the tax advantages of municipal bonds.
- Know the difference between GO bonds and Revenue bonds.
- Be familiar with risks, pricing, and special types like VRDOs.
- Grasp tax-equivalent yield calculations for client recommendations.
- Recognize how AMT impacts private activity bonds.
🎓 Want to master more Series 7 topics with easy summaries and full practice exams?
Check out
👉 https://finra-exam-mastery.com
Study smart. Pass confidently. Get licensed faster!
