Portfolio Management – Series 7 Exam
- April 1, 2025
- Posted by: 'FINRA Exam Mastery'
- Category: Finance
🧾 Portfolio Management – Series 7 Exam
📘 Key Concepts You Must Know for Portfolio Management on the Series 7
Portfolio management is a critical section of the Series 7 exam. Questions often test your understanding of how to allocate assets, assess client profiles, and apply investment strategies based on risk and return objectives. Here’s a clean and focused summary to sharpen your preparation for the portfolio management topics.
🎯 1. Investment Objectives and Client Profiles
Successful portfolio management begins with understanding the client’s investment objectives, including:
| Objective | Primary Focus | Example Investments |
|---|---|---|
| Preservation of Capital | Minimize loss | Treasury securities, money market funds |
| Income | Generate regular cash flow | Bonds, preferred stocks, dividend stocks |
| Growth | Increase portfolio value | Common stocks, equity mutual funds |
| Speculation | High risk for high return | Options, penny stocks, leveraged ETFs |
| Tax Minimization | Reduce tax burden | Municipal bonds, tax-managed funds |
📌 Key Tip: Always match the recommendation to the client’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment goals.
🎯 2. Asset Allocation and Diversification
Asset allocation involves dividing a portfolio among different asset classes to balance risk and reward according to the investor’s goals.
- Strategic Asset Allocation: Long-term fixed percentage across asset classes.
- Tactical Asset Allocation: Short-term adjustments based on market conditions.
Diversification reduces unsystematic risk by spreading investments across various securities, industries, or asset classes.
📌 Key Tip:
- Stocks + Bonds + Cash = Basic diversification.
- Within stocks: Different sectors (tech, health care, utilities) for deeper diversification.
🎯 3. Risk and Return Concepts
| Type of Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Systematic Risk | Market risk – cannot be diversified away (interest rates, inflation, recessions) |
| Unsystematic Risk | Company/industry-specific risk – can be reduced through diversification |
| Liquidity Risk | Difficulty selling assets quickly without losing value |
| Inflation Risk | Erosion of purchasing power |
| Reinvestment Risk | Risk that future proceeds will be reinvested at lower rates |
Expected Return = Weighted average of possible returns based on probability.
🎯 4. Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT)
MPT focuses on constructing portfolios to maximize expected return for a given level of risk.
- Efficient Frontier: Set of optimal portfolios offering the highest expected return for a defined level of risk.
- Correlation: Combining assets with low or negative correlation improves diversification.
📌 Key Tip: Perfect diversification = combining assets that move in opposite directions.
🎯 5. Portfolio Rebalancing
Over time, portfolios drift from original allocations due to market movements.
- Periodic Rebalancing: Reset to target allocations at regular intervals (e.g., yearly).
- Threshold Rebalancing: Reset when an asset class exceeds a set deviation (e.g., +/- 5%).
Benefit: Maintains risk profile aligned with client’s objectives.
🎯 6. Key Formulas You Must Know
- Current Yield (for bonds):
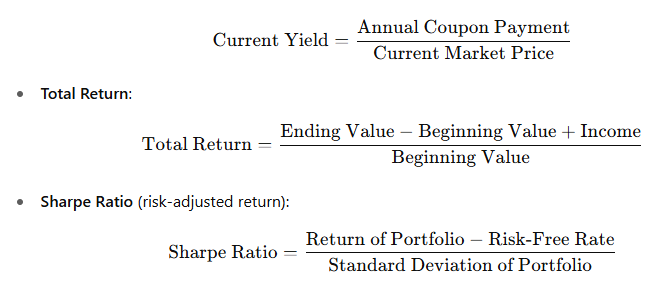
🚀 Conclusion: Mastering Portfolio Management for Series 7
Focus on understanding:
- How client goals dictate portfolio choices
- Why asset allocation and diversification matter
- How to manage different types of investment risk
- Core formulas like current yield and total return
Mastering portfolio management is crucial not just for the Series 7, but for building client trust and managing real-world portfolios.
🎓 Need full Series 7 study tools, practice exams, and flashcards?
Start now at
👉 https://finra-exam-mastery.com
Learn smarter. Pass faster. Build your future in finance!
