Series 7 Bond Math Cheat Sheet
- April 1, 2025
- Posted by: 'FINRA Exam Mastery'
- Category: Finance
🧾 Series 7 Bond Math Cheat Sheet
🎓 Key Formulas and Concepts for Bond Math on the Series 7 Exam
Bond math is a crucial component of the Series 7 exam. Understanding bond pricing, yields, and calculations can be complex, but with the right formulas and concepts, you can simplify the process. Here’s a cheat sheet to help you master bond math for the Series 7 exam.
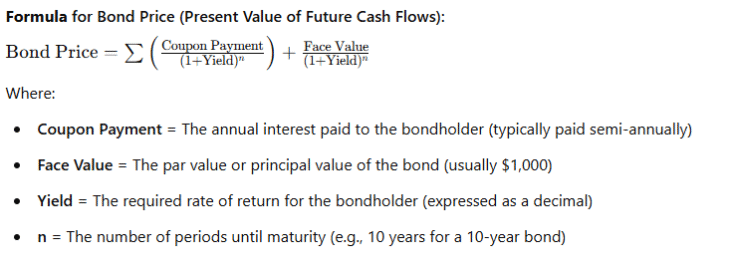
🎯 1. Bond Price
The price of a bond is calculated based on the present value of its future cash flows. A bond’s cash flows consist of coupon payments and the face value (par value) repaid at maturity.
🎯 2. Current Yield
The current yield is the annual coupon payment divided by the current price of the bond.
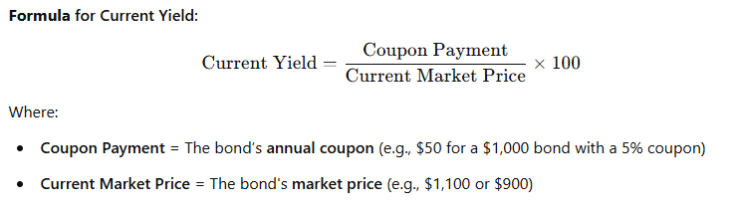
🎯 3. Yield to Maturity (YTM)
The Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the total return expected on a bond if it is held until maturity. YTM includes the bond’s coupon payments and any capital gains or losses from the bond’s price change.

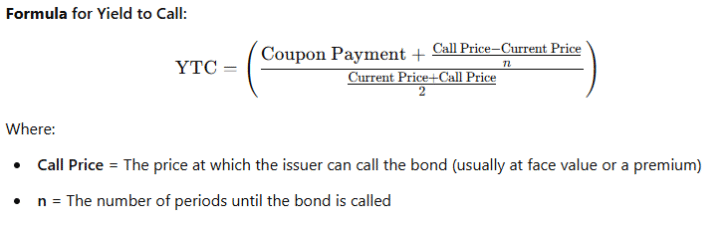
🎯 4. Yield to Call (YTC)
The Yield to Call (YTC) is similar to YTM but assumes that the bond is called (redeemed by the issuer) before maturity. This typically happens if interest rates decline, and the issuer calls the bond to refinance at a lower rate.
🎯 5. Price-Yield Relationship
The relationship between bond price and yield is inversely proportional. When bond yields rise, bond prices fall, and when yields fall, bond prices rise.
- Bond Price ↑ = Yield ↓
- Bond Price ↓ = Yield ↑
This inverse relationship is key when analyzing the impact of changing interest rates on bond prices.
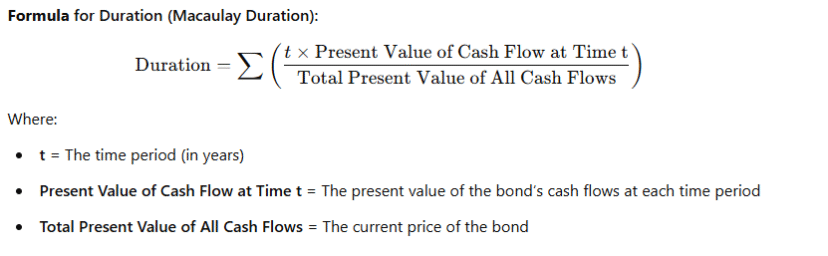
🎯 6. Duration
Duration measures a bond’s sensitivity to interest rate changes and represents the average time it takes for an investor to receive the bond’s cash flows. Bonds with higher durations are more sensitive to interest rate changes.
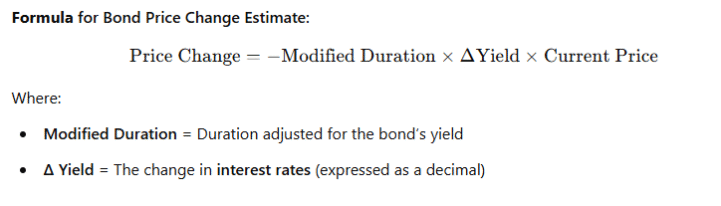
🎯 7. Bond Price Change Estimate (Modified Duration)
To estimate the bond price change for a given change in interest rates, use modified duration.
🎯 8. Discount and Premium Bonds
- Discount Bond: A bond is selling at a discount when its market price is below par value. This typically occurs when the bond’s coupon rate is lower than the prevailing interest rates.
- Discount Bond Price < Par Value
- YTM > Coupon Rate
- Premium Bond: A bond is selling at a premium when its market price is above par value. This usually occurs when the bond’s coupon rate is higher than the prevailing interest rates.
- Premium Bond Price > Par Value
- YTM < Coupon Rate
🚀 Conclusion: Mastering Bond Math for the Series 7 Exam
Understanding bond math is essential for your success on the Series 7 exam. By mastering these key formulas and concepts, you’ll be able to confidently answer questions related to bond pricing, yields, and duration. Regular practice with these formulas will help you better navigate bond-related questions on the exam.
🎓 Need more practice with bond math for the Series 7 exam?
Access study materials, practice exams, and detailed explanations at
👉 https://finra-exam-mastery.com
Prepare with confidence and pass your Series 7 exam!
